What Is Behavioral Targeting in Modern Marketing
Ever heard of behavioral targeting? If you’ve ever looked at a pair of shoes online and then seen ads for those exact shoes follow you around the internet, you’ve experienced it firsthand.
It’s a way of using a person’s online behavior—the pages they browse, the things they search for, the products they add to their cart—to show them ads that are actually relevant. Think of it less like a billboard and more like a personal shopper for the web. Instead of blasting everyone with the same generic message, it pays attention to what you’re interested in and serves up suggestions you might genuinely like.
Unpacking the Power of Personalized Advertising

At its core, behavioral targeting is about moving away from a one-size-fits-all approach and toward a real, personalized conversation. It’s built on the simple idea that every user is different, with their own unique interests, needs, and buying signals. Why shout the same message to a crowded room when you can whisper a helpful suggestion to the right person at the perfect moment?
This technique works by anonymously collecting little bits of data about a user's journey online. It’s not about knowing your name or where you live; it’s about understanding your digital “body language.” Some of the key signals include:
- Browsing History: Pages you’ve visited and products you’ve checked out.
- Search Queries: The exact terms you’ve typed into a search engine.
- Purchase Data: Things you’ve bought in the past or left in your shopping cart.
- Engagement Metrics: Content you’ve clicked, videos you’ve watched, or how long you’ve spent on a page.
The Shift to Smarter Marketing
From all these signals, an anonymous but detailed user profile starts to take shape. Imagine someone who often reads hiking blogs, searches Google for "best waterproof boots," and recently bought a new backpack. It's a pretty safe bet they're an outdoor enthusiast.
Behavioral targeting empowers a sporting goods company to show that specific person an ad for a new high-tech tent, rather than just a generic ad for their entire store. It’s a smarter way to connect.
This approach has become a fundamental part of modern digital marketing. It’s an evolution from simply placing ads on relevant websites (contextual advertising) to targeting an individual based on their actual, demonstrated interests. If you want to go deeper on the nuts and bolts, check out a comprehensive guide to behavioral targeting.
The whole idea is simple but powerful: Past behavior is the best predictor of future intent. When you understand what someone is already interested in, you can deliver something valuable instead of just adding to the noise.
The market for this strategy shows just how effective it is. Valued at roughly $10.5 billion in 2023, the behavioral targeting market is on track to nearly triple, hitting a projected $29.8 billion by 2032.
That explosive growth is fueled by our increasingly digital world and huge leaps in AI that make this kind of personalization more accurate than ever. It’s clear that for any business serious about connecting with customers in a meaningful way, this is no longer just an option—it’s essential.
How We Moved From Context to Behavior

To really get why today’s online experience is so personalized, it helps to rewind and see how digital advertising got its start. Back in the early days of the internet, things were a lot simpler—and a lot less precise.
The go-to strategy was contextual advertising. It worked by placing ads on websites based only on what the page was about. If you were reading a blog about digital cameras, you’d see an ad for a new camera. Simple enough. It was like putting a car ad in a car magazine—it made sense, but it also made a huge assumption that every single person visiting was a hot prospect.
This old-school method targeted the page, not the person. It had no way of knowing if you were a pro photographer researching new gear, a student writing a paper, or just someone who clicked the wrong link. Everyone saw the same ad, which meant a ton of wasted ad dollars and irrelevant ads for most people.
The Rise of People-Focused Advertising
The game really changed when new technologies came along, especially the browser cookie. These tiny data files let websites remember who was visiting and track what they did over time. All of a sudden, marketers could see not just what page someone was on, but what they’d looked at before.
That was the birth of true behavioral targeting. Instead of guessing someone’s interests from a single page, marketers could now build a much richer picture based on their past actions. This evolution, which started picking up steam in the early 2000s, completely flipped the industry on its head. The focus shifted from the page’s content to the user’s activity. You can learn more about the history of behavioral analytics from Grand View Research.
This was a fundamental shift from a "one-to-many" broadcast model to a "one-to-one" conversation. The goal wasn't just to get seen anymore—it was to be seen by the right person with the right message.
This transition paved the way for the personalized web we all use today. A few key technologies powered this change:
- Browser Cookies: Small text files stored on your computer that track your activity on a website or even across different sites.
- Tracking Pixels: Tiny, invisible graphics on web pages or in emails that signal when you’ve visited a page or opened a message.
- Device IDs: Unique codes for mobile devices that allow for tracking and targeting inside apps.
By pulling together and analyzing data from these sources, advertisers could finally start to understand the individual behind the screen. This opened the door for more meaningful, helpful, and effective advertising.
The Step-by-Step Process of Behavioral Targeting
To really get what behavioral targeting is, it helps to think of it as a three-act play that happens in milliseconds. It kicks off the moment you land on a website and wraps up with that perfectly placed ad you see just moments later. Let's follow a user, Alex, who's on the hunt for new running shoes, to see how it all unfolds.
The whole system is built on a constant flow of information, starting with raw data collection and ending with a hyper-relevant ad.
This visual shows exactly how those anonymous user actions get turned into personalized advertising experiences.
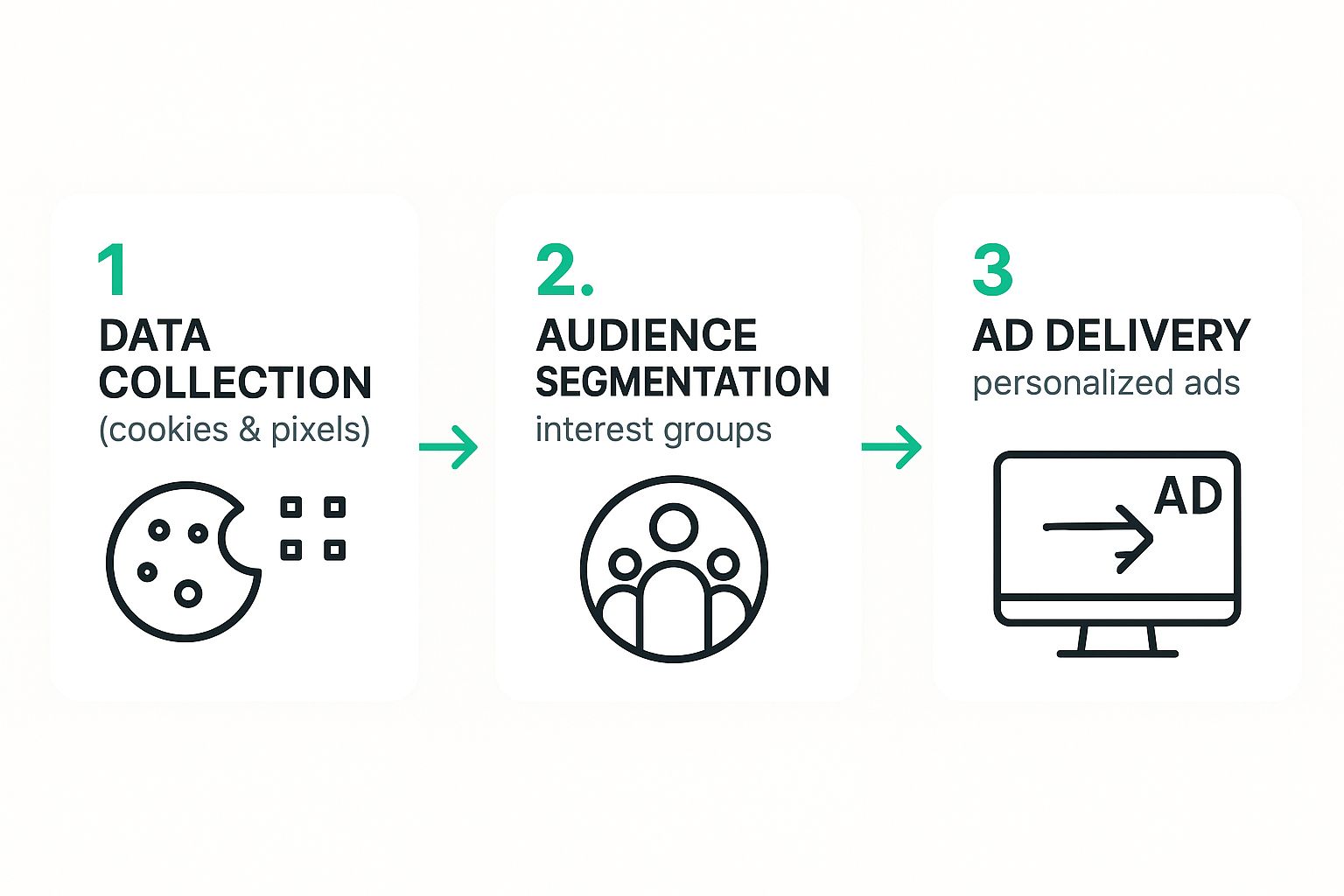
As the infographic lays out, the process is a clear progression: anonymous data points are sorted into organized audience groups, which then makes precise ad delivery possible.
Stage One: Data Collection
The process begins by quietly gathering anonymous data about user behavior. This is all done with small bits of technology that work in the background. When Alex visits a few different e-commerce sites to compare trail running shoes, these tools spring into action.
The key data collection tools are:
- Browser Cookies: These are tiny text files stored on a user's device. They remember activity, like which products Alex looked at or added to his cart.
- Tracking Pixels: These are microscopic, invisible graphics embedded on websites or in emails. They signal when a user has visited a page or taken a specific action, confirming Alex’s interest in running gear.
It's important to remember that this information is completely anonymous. It doesn’t include personal details like names or email addresses—it just creates a digital footprint of interests and intent signals.
Stage Two: Audience Segmentation
With the data collected, the next step is to analyze and sort it all. The system doesn't know Alex personally, but it definitely recognizes his patterns. His behavior—visiting running blogs, searching for "best stability running shoes," and comparing specific brands—gets him placed into a specific audience segment.
This segment might be called something like "Running Enthusiasts" or "In-Market for Athletic Footwear." Segmentation is what allows advertisers to group users with similar interests and buying intentions, making their campaigns way more efficient.
At its heart, segmentation is about finding the signal in the noise. It transforms millions of individual clicks and page views into a clear picture of what a specific group of people is interested in right now.
Stage Three: Ad Delivery
This is the final step, where the magic happens. A little later, Alex is browsing an unrelated news website, and an automated ad auction takes place behind the scenes. Ad networks see that a user from the "Running Enthusiasts" segment is on the page.
Because Alex fits their target profile, a sporting goods company bids to show him an ad. The result? Alex sees a promotion for the exact running shoes he was just researching. This process, known as real-time bidding (RTB), makes sure the most relevant ad is delivered to the right person at the perfect moment.
Efficiently identifying these high-intent users is a core challenge, and learning more about AI lead generation tools can offer deeper insights into automating this process at scale.
A Win-Win for Brands and Customers
When behavioral targeting is done right, it creates a powerful win-win. It’s a huge value add for both the businesses running the ads and the people seeing them. The whole dynamic shifts from a disruptive, shouty broadcast into a genuinely helpful conversation.
For brands, the advantages are direct and easy to measure. By focusing ad spend only on people who have shown real interest, businesses see a much higher return on their investment. Instead of throwing money at a wide, indifferent audience, every dollar goes toward reaching a warm lead.
That kind of precision leads to much better outcomes.
Driving Business Growth
Showing someone a relevant ad isn't just about being efficient; it’s about being effective. When an ad feels more like a helpful suggestion than a random interruption, people are far more likely to actually engage with it.
This leads to some key business benefits:
- Higher Conversion Rates: Showing the right product to the right person at the right time dramatically increases the chance of a purchase.
- Improved Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): Companies spend less to get each new customer because their marketing is hyper-focused on users with clear intent to buy.
- Stronger Customer Loyalty: A personalized experience makes customers feel seen and understood. This builds a positive vibe around the brand and encourages them to come back again and again.
The numbers back this up. A recent Deloitte study found that 80% of consumers prefer brands that offer personalized experiences. Even better, these shoppers spend 50% more on average with brands that personalize compared to those that don’t. You can dig deeper into the impact of personalization on consumer behavior at Amplitude.
Creating a Better Customer Experience
From the customer’s point of view, the benefits of behavioral targeting often just feel like a cleaner, more relevant online journey. The most obvious perk is seeing fewer annoying and totally irrelevant ads.
Instead of being bombarded with promotions for things they’d never dream of buying, users discover stuff they actually find interesting or useful. This makes browsing the web feel less cluttered and more fine-tuned to their specific needs.
For the customer, effective behavioral targeting feels less like being advertised to and more like receiving a timely, helpful recommendation from a savvy personal shopper.
Ultimately, this strategy helps people find what they’re looking for faster and more efficiently. Whether it's discovering a new hobby, finding a solution to a problem, or getting a deal on something they were already thinking about, a personalized ad can add real value. This mutual benefit is the core reason why what is behavioral targeting has become such a fundamental part of how the modern internet works.
Behavioral Targeting Examples You See Every Day

Behavioral targeting isn't some abstract marketing term—it's woven into the fabric of your daily digital life. The world’s biggest brands have mastered this strategy, using it to craft personalized experiences that feel so natural you barely notice them.
Once you know what to look for, you’ll see it everywhere. From the products Amazon suggests to the shows Netflix queues up for you, your past actions are constantly shaping your future online experiences.
Let's pull back the curtain on a few of the most powerful examples you probably see every single day.
Amazon: The undisputed King of Recommendations
Amazon's recommendation engine is a masterclass in behavioral targeting. It’s not just tracking what you buy; it's watching everything. It sees what you look at, what you add to your cart (even if you abandon it), and how long you linger on a specific product page.
All that data fuels its famous "Customers who bought this item also bought" and "Inspired by your browsing history" sections. By analyzing the behaviors of millions of shoppers, Amazon can make spookily accurate predictions about what you might want next. This isn't just a neat feature—it reportedly drives 35% of its total revenue.
Amazon's entire model proves a simple truth: past behavior is the best predictor of future intent. Their system turns your clicks and purchases into a storefront built just for you.
Netflix: Your Personal Movie Theater
Ever wonder how Netflix just knows what you’re in the mood to watch? The second you log in, its algorithm gets to work, completely redesigning your homepage based on your viewing history.
It tracks everything:
- Shows you’ve watched (and how much you watched before you stopped).
- Genres you love and the actors you seem to follow.
- The time of day you usually settle in for a binge-watch.
- Even the titles you browse but ultimately decide to skip.
This treasure trove of behavioral data allows Netflix to do more than just recommend shows. It will even show you different promotional artwork for the same movie just to appeal to your specific tastes. It’s a brilliant way to cut through the noise and keep you glued to the screen.
Understanding this kind of subtle user sentiment is also the foundation of good social media reputation monitoring, where brands listen to online conversations to get a real feel for public opinion. By figuring out what keeps you clicking "play," Netflix makes the experience feel uniquely yours, making you far more likely to stick around.
Behavioral Targeting Strategies in Action
To see just how widespread this is, let's break down how a few other major platforms put behavioral data to work. Each one collects different signals to deliver a uniquely personalized experience.
| Platform | Data Signals Used | Personalized Outcome For User |
|---|---|---|
| Spotify | Listening history, skipped songs, playlist creations, time of day | Curated playlists like "Discover Weekly" and "Daily Mixes" that feel hand-picked. |
| Clicks, likes, shares, group memberships, time spent on posts | A news feed showing content from friends and brands you're most likely to engage with. | |
| YouTube | Videos watched, channels subscribed to, search history, comments | A homepage and "Up Next" queue filled with videos tailored to your viewing habits and interests. |
| TikTok | Videos watched to completion, likes, shares, accounts followed | The "For You Page" (FYP) algorithm, which delivers an endless, hyper-personalized stream of content. |
As you can see, the goal is always the same: use past actions to create a more relevant and engaging future experience. These platforms aren't just showing you random content; they're showing you what their data says you want to see, long before you even know it yourself.
Navigating Privacy Concerns and Best Practices
The power that comes with behavioral targeting is a huge responsibility. The moment you start collecting user data, you’re stepping into a world of consumer privacy expectations and some pretty complex regulations. For a lot of people, the whole idea of their online activity being tracked feels invasive, and frankly, it raises some important questions about transparency and control.
This is exactly why a trust-first approach isn't just about doing the right thing—it's smart business. You simply can't afford to ignore privacy anymore. Major regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) have set tough new standards for how companies must handle personal data.
These laws are all about empowering consumers, giving them the right to know what data is being collected and the ability to opt out. That means companies have to prioritize clear communication and get user consent just to operate legally and keep customers from walking away.
Adopting Privacy-First Best Practices
To handle this responsibly, your behavioral targeting strategies need to be built on a foundation of transparency and user control. It’s all about making your data practices easy for anyone to understand and giving people simple ways to manage their own preferences.
Here are a few essential practices to get you started:
- Maintain a Clear Privacy Policy: Write your privacy policy in plain English, not a bunch of legal jargon. Clearly explain what data you collect, why you collect it, and how you use it for advertising. To see what this looks like in practice, you can learn more about our own comprehensive Intently privacy policy.
- Provide Simple Opt-Out Mechanisms: Don't bury the "unsubscribe" or "manage preferences" links deep in your site. Make it incredibly easy for users to take control of their data or opt out of targeted advertising altogether.
- Prioritize Data Anonymization: Whenever you can, use anonymized or aggregated data for your audience segmentation. This protects individual identities while still letting you spot valuable behavioral trends.
The core idea is simple: be the kind of company you'd want to buy from yourself. Treat user data with the same respect you'd expect for your own, and you'll end up with a more loyal and trusting customer base.
Preparing for a Cookieless Future
The entire industry is in the middle of a massive shift away from third-party cookies, which have been the engine behind behavioral targeting for years. This "cookieless future" is forcing marketers to get creative and find new, privacy-friendly ways to deliver a personal touch.
This change means a much bigger focus on first-party data—that’s the information customers willingly share directly with a brand. It's also critical to understand the new regulatory frameworks popping up. For instance, Ad360's approval within the IAB's New Data Privacy Framework shows a real commitment to keeping up with these evolving standards.
By embracing transparency and focusing on building direct relationships, businesses can keep delivering real value to customers without crossing any privacy lines.
Frequently Asked Questions
When you start digging into behavioral targeting, a lot of practical and ethical questions pop up. Let's clear the air and tackle some of the most common ones so you have a full picture of how it all works.
Key Distinctions and Definitions
It's easy to get behavioral targeting mixed up with other ad strategies. The main thing to remember is that it’s about the person, not the place.
Is behavioral targeting the same as contextual targeting?
Nope, they're completely different animals. Contextual targeting is all about the environment—it puts a camera ad on a photography blog because the topics match. But behavioral targeting follows the user. It shows that same camera ad to someone who has been searching for camera reviews, even if they're currently reading the news or checking the weather.
Is behavioral targeting legal and ethical?
Yes, it’s legal as long as companies play by the rules, like GDPR and CCPA. These regulations are all about getting user consent and being transparent. The ethical side is a bit more of a gray area. It’s a balancing act between creating a personalized experience and respecting someone's privacy, which is why giving people a clear way to opt out is so important for building trust.
Technical and Future-Facing Questions
Technology doesn't stand still, and neither does behavioral targeting—especially now that old-school tracking methods are on their way out.
The industry's move away from third-party cookies isn't the death of personalization; it's an evolution. The focus is just shifting to privacy-first options that still deliver relevant ads without being creepy.
Can behavioral targeting work without cookies?
Absolutely. The whole industry is moving toward a "cookieless" future. We're already seeing smart alternatives take center stage:
- First-party data: This is information that customers give you directly, like their email address or purchase history. It's gold.
- Privacy-first technologies: New tools are popping up that allow for personalization without the invasive tracking of the past.
- A fresh look at contextual signals: Blending the relevance of a webpage's content with other privacy-safe user data is becoming more common.
How can I see what data is collected about me?
You actually have more control than you might think. Big platforms like Google and Facebook have privacy dashboards where you can see and manage the data they use for ads. Plus, laws like GDPR give you the legal right to ask companies for the data they have on you, putting the power back in your hands.
Ready to turn social conversations into qualified leads? Intently monitors millions of online discussions to find customers with real buying intent, delivering them directly to your team. Start finding your future customers today.